Your step-by-step roadmap to automating revenue recognition and staying audit-ready.
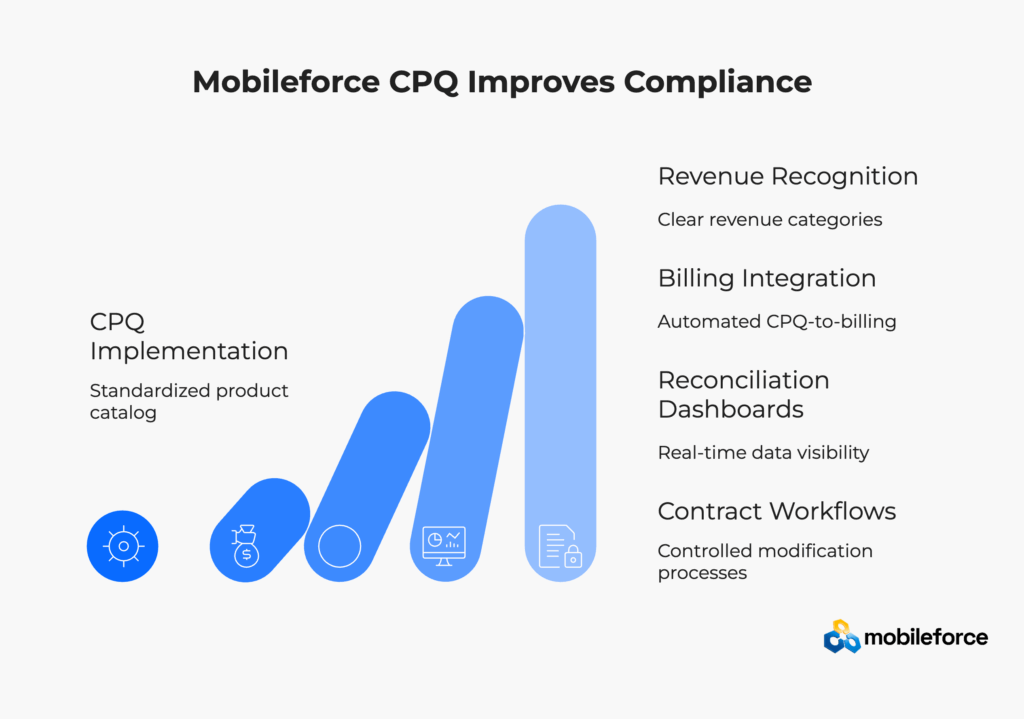
ASC 606 revenue recognition compliance requires capturing performance obligations and contract economics at the quote stage, not after deals close. CPQ software serves as the critical control point, automating data flow from quotes through revenue recognition while maintaining audit trails. Companies implementing CPQ-driven revenue processes see 78% fewer manual adjustments, 4-day faster month-end close, and eliminated material audit findings. Key success factors: proper system architecture, comprehensive data mapping, and integrated quote-to-cash workflows.
“The CFO of a Fortune 500 manufacturing company told me last month: ‘Attempting revenue recognition compliance without integrated CPQ is like performing surgery with a butter knife – you might survive, but why risk it?'”

ASC 606, officially known as Revenue from Contracts with Customers, represents the most significant accounting change in decades. This revenue recognition standard became effective for public companies in December 2017 and private companies in December 2018. The Financial Accounting Standards Board created a unified framework replacing over 200 pieces of industry-specific revenue recognition guidance.
According to the Securities and Exchange Commission, ASC 606 affects virtually every entity that enters into contracts with customers to transfer goods or services. The standard’s impact extends beyond accounting departments to sales operations, legal teams, and technology infrastructure.
The ASC 606 revenue recognition process follows five critical steps:
Revenue recognition software must capture and track each step throughout the quote to cash process. According to KPMG’s comprehensive 2024 revenue recognition handbook, the Financial Accounting Standards Board’s Post-Implementation Review concluded that ASC 606 meets its intended purpose without significant unintended consequences.
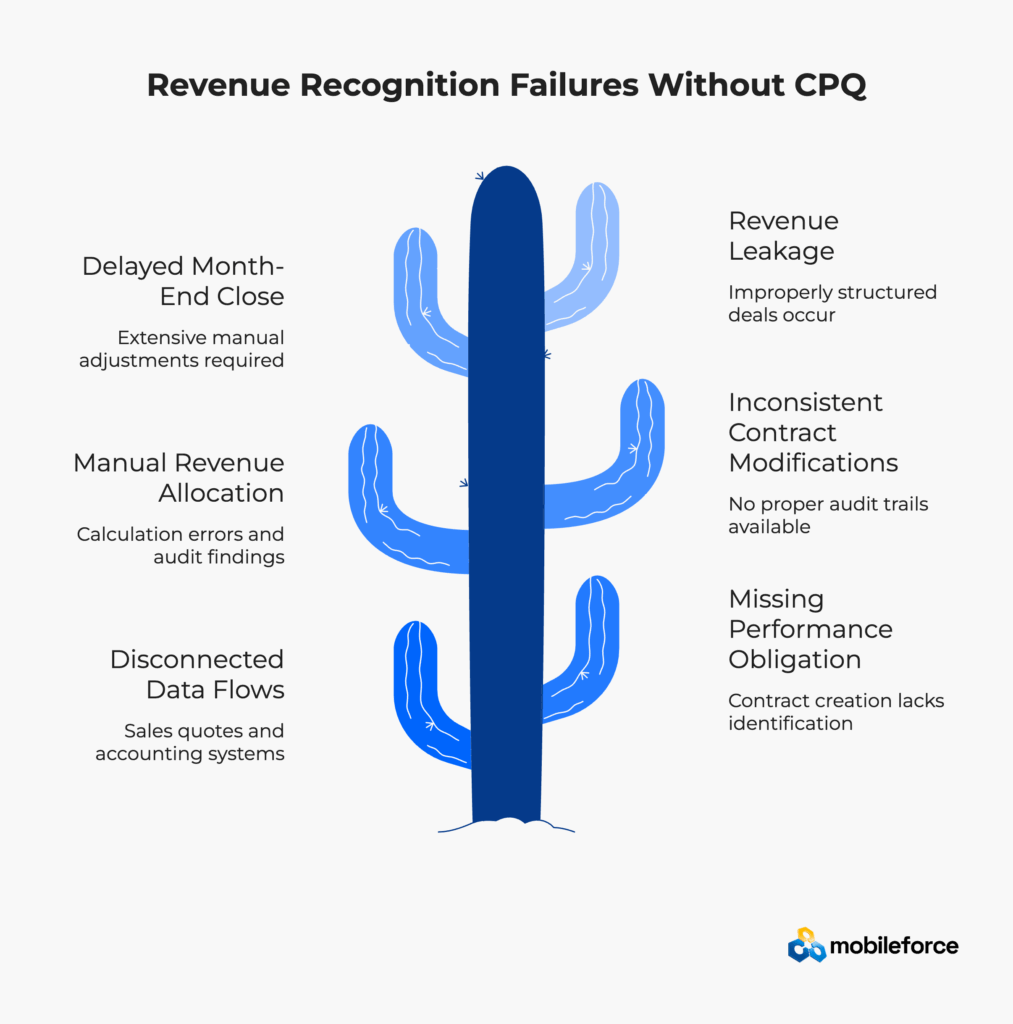
Companies without proper configure price quote systems face critical revenue recognition compliance failures:
Research from the American Institute of CPAs shows that companies with automated quote-to-revenue processes reduce audit-related adjustments by 78% compared to those using manual processes.
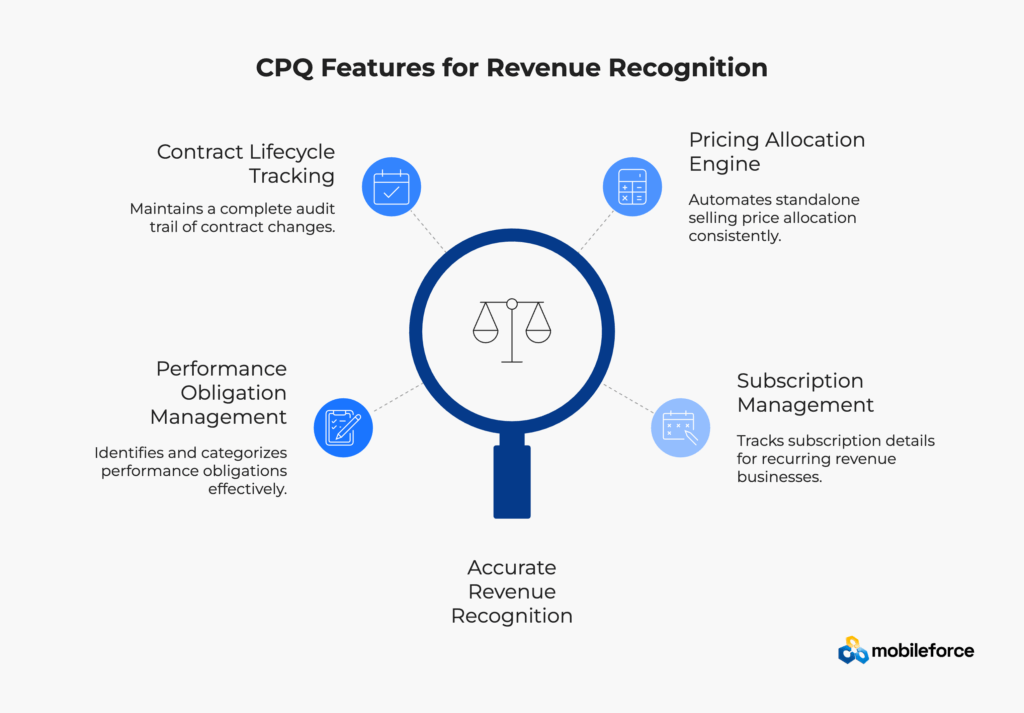
Configure price quote software transforms revenue recognition compliance by establishing controls at the source – the sales quote. Rather than treating revenue recognition as a post-sale accounting function, modern CPQ solutions capture the contract economics necessary for compliant revenue recognition from quote inception.
The Harvard Business Review identifies quote-to-cash automation as a critical capability for modern sales organizations. Research shows that CPQ enables sales teams to send 49% more contracts, proposals, quotes and RFP responses to prospects and customers while maintaining compliance controls.
Performance Obligation Management The CPQ system must automatically identify and categorize performance obligations based on product configurations. This includes distinguishing between software licenses, professional services, maintenance contracts, and subscription services according to ASC 606 criteria.
Contract Lifecycle Tracking From initial quote through amendments, renewals, and cancellations, the CPQ maintains a complete audit trail of all contract changes. This capability is essential for mid-term contract modifications under ASC 606.
Pricing Allocation Engine Automated standalone selling price allocation across performance obligations ensures consistent revenue recognition treatment. The system must handle complex pricing scenarios including volume discounts, multi-year contracts, and bundled offerings.
Subscription Management For recurring revenue businesses, the CPQ must track subscription start dates, billing cycles, proration calculations, and upgrade/downgrade scenarios while maintaining compliance with revenue recognition timing requirements.
|
Architecture Pattern |
Integration Complexity |
Flexibility |
Best For |
Implementation Time |
|
Best-of-Breed |
High (4+ systems) |
Very High |
Complex revenue models |
6-8 months |
|
Unified Platform |
Low (2 systems) |
Medium |
Standard business models |
3-4 months |
|
Hybrid Approach |
Medium (3 systems) |
High |
Mixed complexity needs |
4-6 months |
Key insight: Best-of-breed approaches offer maximum flexibility for complex revenue recognition requirements, while unified platforms accelerate implementation for standard business models.
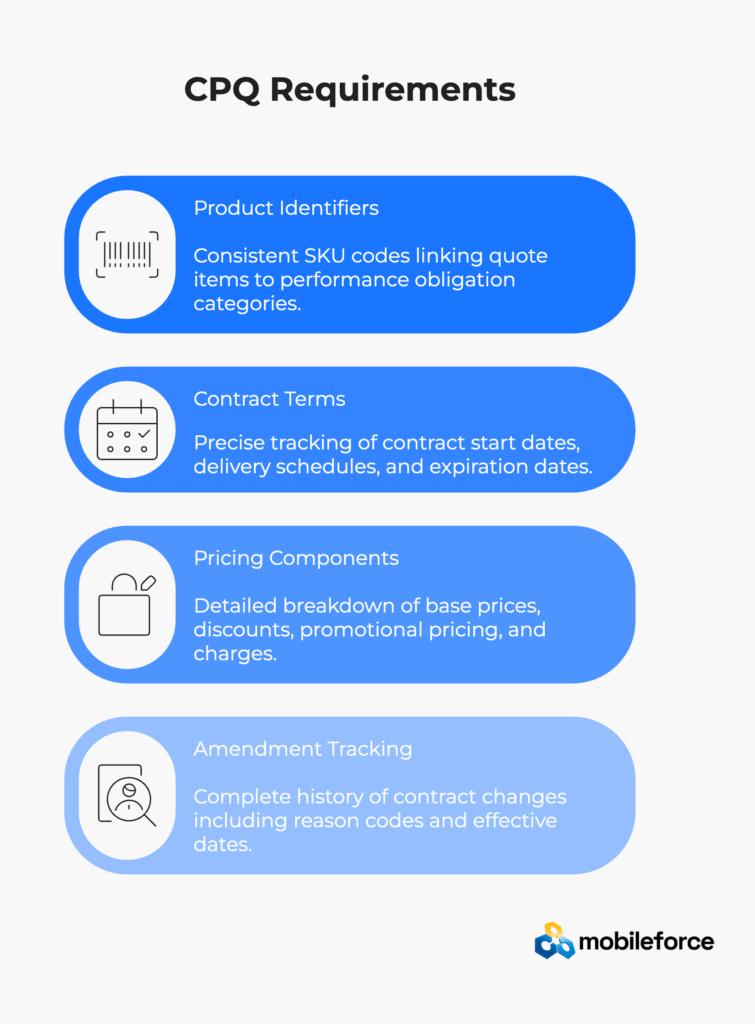
Product and Service Identifiers Consistent SKU codes linking quote items to performance obligations categories. The CPQ must distinguish between different revenue recognition patterns such as point-in-time versus over-time recognition according to ASC 606 guidance.
Contract Terms and Dates Precise tracking of contract start dates, performance obligation delivery schedules, and contract expiration dates. This includes handling complex scenarios like phased deliveries and milestone-based recognition.
Pricing Components and Allocation Detailed breakdown of base prices, volume discounts, promotional pricing, and one-time versus recurring charges. The system must maintain allocation metadata for audit purposes as required by FASB ASC 606-10-32-28.
Amendment and Modification Tracking Complete history of contract changes including reason codes, effective dates, and impact on revenue recognition schedules. This is particularly important for subscription businesses with frequent plan changes.
|
Data Element |
CPQ Capture |
Billing System |
Revenue Recognition |
Criticality |
|
Performance Obligations |
✓ Required |
✓ Reference |
✓ Primary Driver |
Critical |
|
Contract Start/End Dates |
✓ Required |
✓ Required |
✓ Recognition Trigger |
Critical |
|
Pricing Allocation |
✓ Calculate |
✓ Invoice Basis |
✓ Recognition Basis |
Critical |
|
Amendment History |
✓ Track Changes |
✓ Update Billing |
✓ Recompute Revenue |
High |
|
Customer Information |
✓ CRM Integration |
✓ Billing Entity |
✓ Reporting |
Medium |
Summary: Performance obligations, contract dates, and pricing allocation require critical data flow between all systems, while amendment tracking maintains high importance for compliance audit trails.
See how Mobileforce’s subscription CPQ captures all revenue recognition data elements automatically.
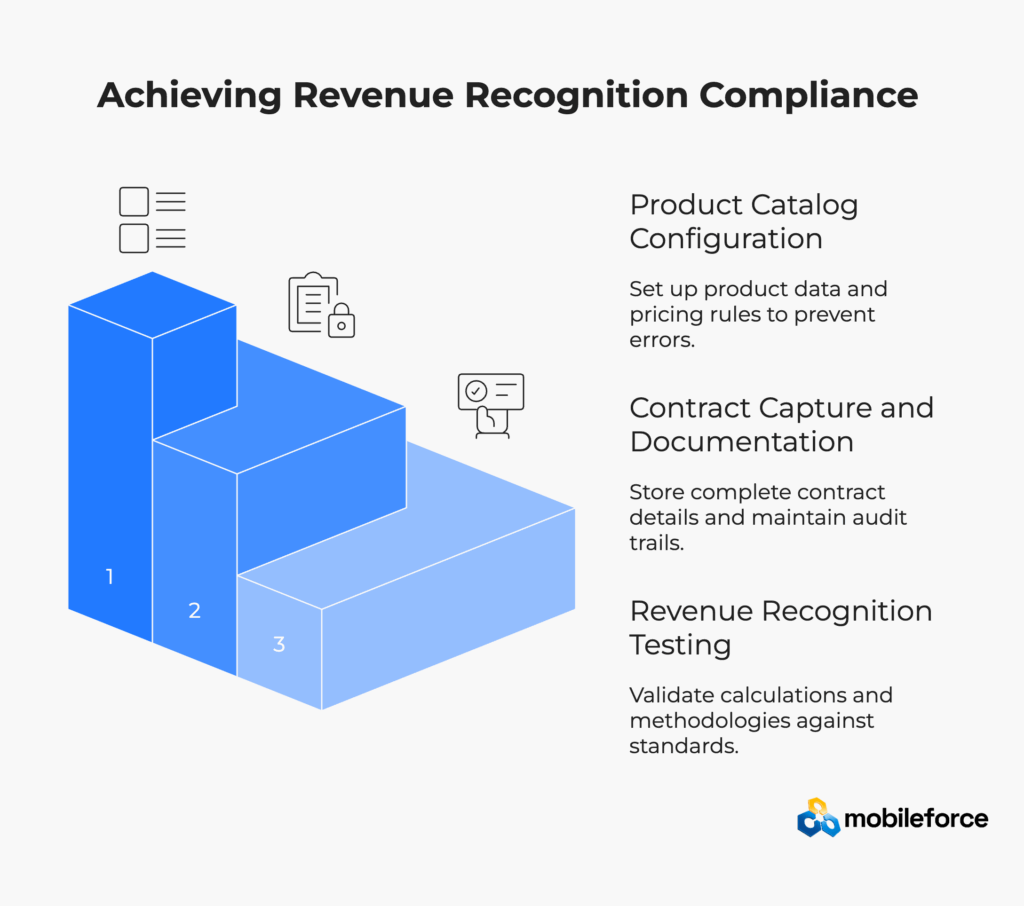
Configure product master data with clear performance obligation categories. Establish separate SKUs for software licenses, professional services, training, maintenance, and support. Document standalone selling price methodologies for each product category according to ASC 606-10-32-32 requirements.
Critical Controls:
Store complete contract documentation including all terms, conditions, and amendments. Maintain immutable audit trails of all contract events with timestamp and user identification. Implement electronic signature workflows that preserve legal enforceability.
Essential Elements:
Revenue Recognition Testing and Validation
Establish testing protocols for revenue recognition calculations before system go-live. Validate allocation methodologies against accounting standards and auditor requirements. Test edge cases including contract modifications, terminations, and multi-element arrangements.
According to the latest BDO guidance on ASC 606, companies with comprehensive implementation controls report significantly fewer audit findings and faster month-end close processes.
A $120 million industrial equipment manufacturer struggled with complex revenue recognition compliance across multiple product lines. Their quotes included equipment sales, installation services, training programs, and maintenance contracts – each representing different performance obligations with varying recognition patterns.
Implementation Results Summary
|
Metric |
Before Implementation |
After Implementation |
Improvement |
|
Month-end Close Time |
11 days |
7 days |
4-day reduction |
|
Manual Journal Entries |
120+ quarterly |
27 quarterly |
78% reduction |
|
Audit Findings |
Material weakness |
Clean opinion |
Eliminated |
|
Quote-to-Invoice Time |
8 days average |
2 days average |
75% improvement |
|
Revenue Recognition Accuracy |
87% |
99.2% |
12.2% improvement |
Key insight: Automated CPQ-driven revenue recognition processes delivered measurable improvements across all compliance and efficiency metrics while eliminating material audit weaknesses.
Solution Implementation
Working with Mobileforce CPQ, the company implemented:
This transformation aligns with KPMG’s guidance emphasizing the importance of capturing proper contract economics from the beginning of the sales process rather than treating revenue recognition as a post-sales accounting exercise.
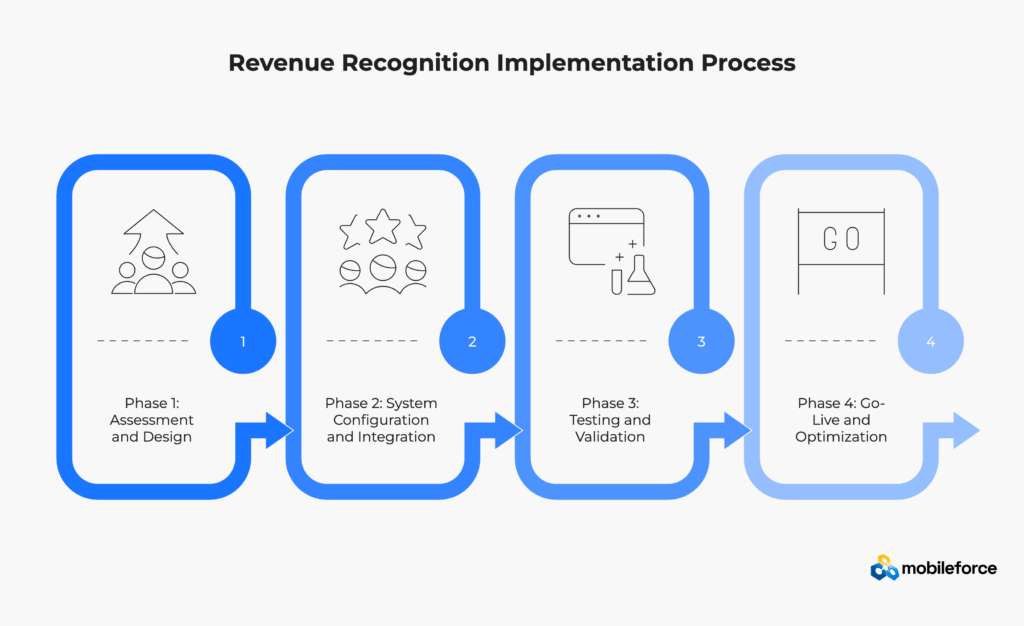
Conduct comprehensive current state analysis of quote-to-revenue processes. Map existing performance obligation identification methods and revenue allocation approaches. Identify gaps between current processes and ASC 606 requirements.
Key Activities:
Configure CPQ system with revenue recognition focus including product catalog setup, pricing rules, and workflow definitions. Establish integrations between CPQ, billing, and revenue recognition systems.
Implementation Focus:
Execute comprehensive end-to-end testing including quote generation, billing integration, and revenue recognition calculation validation. Test contract modification scenarios ensuring proper handling of upgrades, downgrades, and cancellations.
Testing Scenarios:
Execute production cutover with shadow period for validation. Monitor system performance and adjust configurations as needed. Establish continuous improvement processes for ongoing optimization.
Success Metrics:
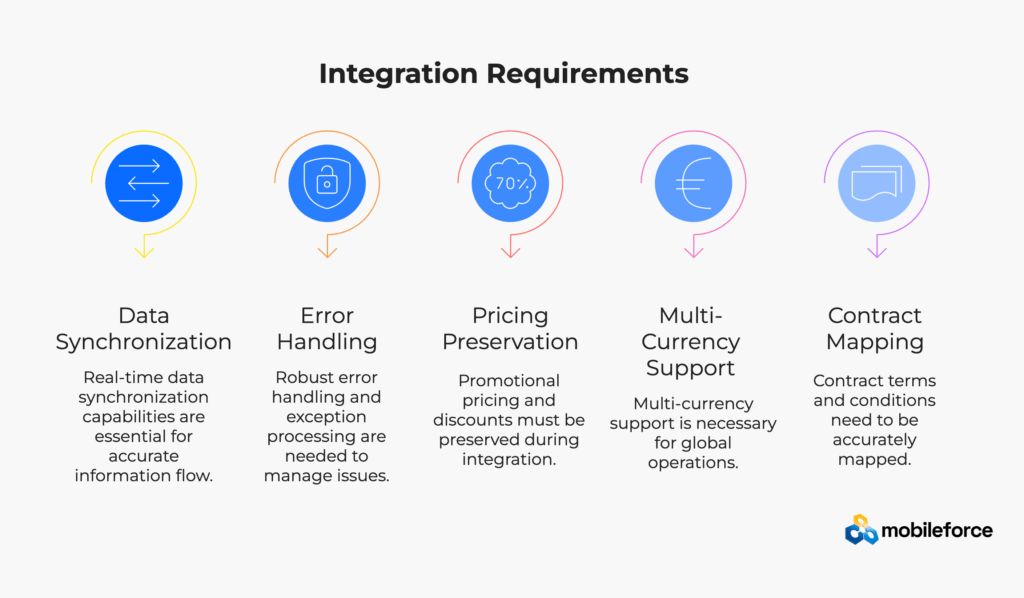
Ensure quote details including performance obligations, pricing allocation, and contract terms flow accurately to billing systems. According to Deloitte’s quote-to-cash research, companies with automated quote-to-billing integration reduce revenue leakage by an average of 3-5%.
Integration Requirements:
Verify that invoices correctly reference original quote and order data maintaining audit trail integrity. Ensure that billing events trigger appropriate revenue recognition entries based on performance obligation fulfillment.
Critical Elements:
According to CPQ implementation research, companies with proper integrations see 26% more sales representatives meeting quotas while maintaining compliance requirements.
|
Feature |
Manual Process |
Basic CPQ |
Mobileforce CPQ |
|
Performance Obligation ID |
Manual Review |
Basic Rules |
Automated Intelligence |
|
Contract Amendment Tracking |
Spreadsheets |
Limited History |
Complete Audit Trail |
|
Pricing Allocation |
Manual Calculation |
Simple Rules |
Advanced Algorithms |
|
Offline Capability |
Not Applicable |
None |
Full Functionality |
|
Integration Flexibility |
Custom Development |
Limited APIs |
Pre-built Connectors |
|
Compliance Reporting |
Manual Assembly |
Basic Reports |
Comprehensive Analytics |
Summary: Advanced CPQ solutions provide automated intelligence and comprehensive audit trails compared to manual processes or basic CPQ systems, significantly improving compliance capabilities.
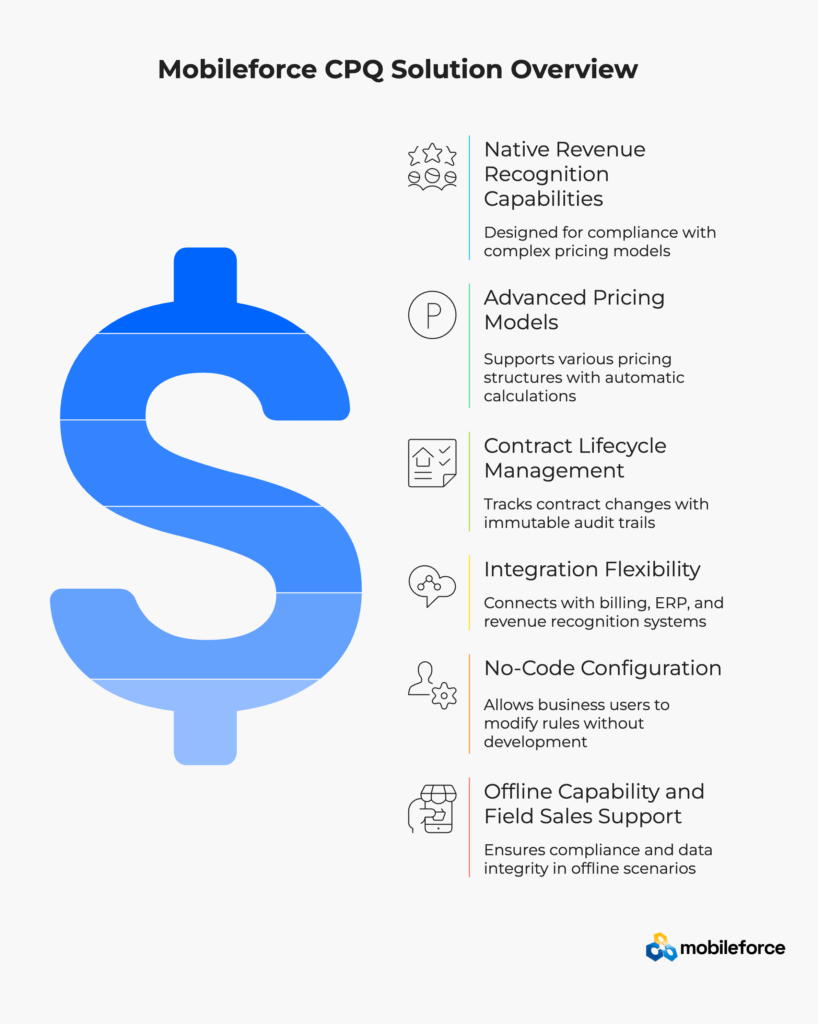
Mobileforce’s CPQ solution was designed with revenue recognition compliance as a foundational capability. The platform provides comprehensive subscription management framework supporting complex pricing models while preserving allocation metadata throughout the quote-to-cash process.
Core Capabilities:
Maintain compliance even when working offline through comprehensive caching and synchronization capabilities. Field sales teams can generate compliant quotes without internet connectivity while ensuring data integrity upon reconnection.
Successful ASC 606 implementations require strong executive sponsorship spanning sales, finance, and legal departments. According to McKinsey research on digital transformations, projects with active executive sponsorship are 5x more likely to succeed.
Key Elements:
Ensure high-quality master data including accurate product catalogs, customer information, and pricing structures. The Data Management Association estimates that poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually.
Critical Activities:
Establish comprehensive monitoring dashboards tracking key compliance metrics including revenue recognition timing, manual adjustment frequency, and audit trail completeness. Configure automated alerts for unusual patterns or potential compliance issues.
Key Performance Indicators:
Conduct regular reviews of revenue recognition processes identifying optimization opportunities. Stay current with accounting standard updates and implementation guidance from regulatory bodies.
According to industry best practices, companies with mature monitoring and optimization processes maintain consistently high compliance levels while minimizing operational overhead.
ASC 606 revenue recognition compliance transforms from overwhelming challenge to competitive advantage when organizations implement proper CPQ-driven processes. The evidence overwhelmingly supports integrated quote-to-cash automation as the foundation for sustainable compliance.
Companies implementing comprehensive CPQ solutions achieve measurable results: 78% reduction in manual adjustments, 4-day acceleration in month-end close processes, and complete elimination of material audit findings. These improvements stem from capturing contract economics at quote inception rather than treating revenue recognition as post-sale accounting cleanup.
The implementation methodology spans four distinct phases over 6-8 months for complex organizations. Success depends on executive sponsorship, comprehensive data mapping, and integrated system architecture connecting CPQ through revenue recognition platforms.
Looking ahead, regulatory requirements continue evolving while business models grow increasingly complex. Organizations with mature CPQ-driven revenue recognition processes position themselves to adapt quickly to future changes while maintaining competitive sales velocity.
The choice becomes clear: invest in proper CPQ infrastructure now, or continue struggling with manual processes that scale poorly and create audit risk. Companies choosing integrated automation report improved sales efficiency alongside compliance confidence.
For organizations ready to transform their revenue recognition processes, the methodology and best practices outlined here provide a proven roadmap. The technology exists, the implementation approaches are tested, and the business case is compelling.
CPQ software enables ASC 606 compliance by capturing performance obligations, contract terms, and pricing allocations at the quote stage. This ensures revenue recognition data flows seamlessly through the quote-to-cash process without manual intervention. According to the FASB’s revenue recognition guidance, capturing these elements from contract inception is essential for compliant revenue recognition.
The ASC 606 five-step model includes:
Wall Street Prep’s ASC 606 guide emphasizes that proper field mapping between systems is essential for automated compliance with each step.
Contract modifications can significantly impact revenue recognition schedules depending on whether they create new contracts or modify existing ones. A properly configured CPQ system captures modification details, maintains version history, and applies correct accounting treatment. The RevenueHub analysis of ASC 606 highlights contract modifications as one of the most challenging compliance aspects.
Critical data includes:
PwC’s revenue recognition handbook emphasizes that complete data mapping is essential for maintaining audit trails.
Yes, under ASC 606, sales commissions must be capitalized and amortized over the period of benefit. An integrated CPQ system can align commission calculations with revenue recognition schedules, ensuring compliance with the contract cost capitalization requirements in ASC 340-40.
Most mid-sized organizations complete ASC 606-compliant CPQ implementations in 4-6 months:
Timeline depends on business model complexity, integration requirements, and existing system maturity.
Common errors include:
HubiFi’s revenue recognition guide provides detailed examples of these compliance pitfalls and prevention strategies.
Revenue recognition compliance requires seamless integration between CPQ, billing, revenue recognition, and general ledger systems. Essential capabilities include:
Key success metrics include:
Ongoing maintenance includes: